Cisco MDS Product Overview
Cisco Systems is one of the major vendors of SAN infrastructures nowadays. Its journey in the world of the storage communications starts back in 2002, when it acquired Andiamo Systems, Inc. Based on the company’s multilayer storage switches, later that year Cisco released its line of FC switches—the Cisco MDS family of switches. The Cisco MDS switches were running a special operating system called the SAN-OS, which was Cisco’s implementation of the Fibre Channel Protocol, based on the standard, but also expanded with some unique features such as the virtual SANs (VSANs). The SAN-OS provided support for multiprotocol and multitransport with a rich set of intelligent network and storage services as well as integrated management applications for efficient storage network administration. There was support not only for the Fibre Channel Protocol but also advanced features such as Fibre Channel Protocol port channels, Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP), Inter-VSAN Routing (IVR), Cisco Discovery Protocol, FICON for IBM Mainframes, and more.
Additionally, in the SAN-OS, and later in the NX-OS, there was interoperability support for when the Cisco MDS FC switches would be deployed in a multivendor environment. There were three interoperability modes supporting the specifics of Brocade, McData, and FCP standards based Fibre Channel switches.
The SAN-OS was running on and managing the purpose-built Cisco MDS switches. There were three separate management tools and options.
The SAN-OS provided a command line interface (CLI), which allowed administrators to connect to the FC switch via a terminal emulator supporting Telnet and SSH. The alternative to the CLI was, and still is, the Device Manager. Figure 10-21 shows screenshots from the Device Managers from different models of Cisco MDS switches.
Figure 10-21 Cisco Device Manager
Device Manager is a graphical user interface (GUI) that supports switch provisioning and provides a graphical representation of the linecard and supervisor modules, ports, power supplies, and so on. Here are some of the features supported:
- Configuring physical Fibre Channel interfaces
- Configuring virtual Fibre Channel interfaces
- Configuring FCoE features
- Configuring zones for multiple VSANs
- Managing ports, port channels, trunking, and oversubscription
- Managing Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3 (SNMPv3) security access to switches
- Managing command line interface (CLI) security access to the switch
- Managing alarms, events, and notifications
- Saving and copying configuration files and software images
- Viewing the hardware configuration
- Viewing the chassis, module, port status, and statistics
The tool for discovering, provisioning, configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting SAN fabrics built with the Cisco MDS and Nexus switches was the Cisco Fabric Manager. Figure 10-22 shows a screenshot from the Cisco Fabric Manager.
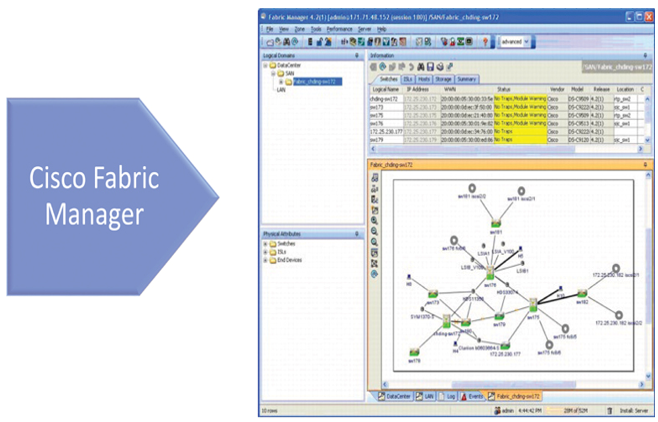
Figure 10-22 Cisco Fabric Manager
Some of the main features were the following:
- Discovery: Cisco Discovery Protocol, Fibre Channel Generic Services (FC-GS), Fabric Shortest Path First (FSPF), and Small Computer System Interface 3 (SCSI-3) for discovery of devices and interconnects on one or more fabrics.
- Automation: Configuration checking, performing successful fabric merges, and resolving configuration inconsistencies automatically. Zone configuration with wizards, Inter-VSAN routing (IVR), FC Port Channels, Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) tunnels, and IP access control lists (ACLs), and Configuration Analysis Tool.
- Monitoring and reporting: Real-time statistics and historical performance monitoring and reporting as well as visibility into the entire Cisco storage network through Cisco Fabric Manager server federation.
Later, with the development of the data center technologies, Cisco released the Nexus family of switches. These switches support not only Ethernet environments but also the Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) protocol. As the FCoE allows FC communication over Ethernet networks, this provided support and flexibility for using different designs in the data centers and led to optimization in the access layer by using Cisco Nexus switches for both Ethernet and SAN communication. This duality in the nature of the Cisco Nexus switches required a new operating system that could support both Ethernet and FC communication. As a result, the NX-OS was released. It is a modular operating system used on the Cisco Nexus and MDS switches. Based on the SAN-OS, the NX-OS module was developed, which is responsible for storage communication.
These developments also affected the Cisco Fabric Manager. As the Cisco MDS and Nexus switches were working together in the new converged designs for the data center infrastructures, there was a need for a provisioning, management, monitoring, and troubleshooting application that could support both the Ethernet and the SAN infrastructures. Thus, the Cisco Fabric Manager evolved as the foundation for the Cisco Data Center Network Manager (DCNM), a management solution for all NX-OS network deployments spanning multitenant, multifabric LAN fabrics, SAN fabrics, and IP Fabric for Media (IPFM) networking in the data center powered by Cisco.
Here are some of the major features supported:
- Fabric management for multiple types of LAN solutions, including VXLAN-EVPN, Cisco Fabric Path, and traditional three-tier LAN deployments
- Day-0 POAP for rapid policy-based bootstrapping of fabric infrastructure
- Auto-detection of unprovisioned switches for use in the Fabric Builder
- Smart topology views showing virtual port channels (vPCs) and virtual device contexts for Cisco Nexus networks (topology views include VXLAN search)
- Resource pooling, such as IP addresses and VXLAN segment IDs to be allocated on a per-fabric basis
- Role-based access control (RBAC) within the fabric to separate administrative tasks between functional domains
- SAN Telemetry function (optional, licensed feature)
- Port monitoring (PMon) configuration
- Historical trend data for SAN Inter-Switch Links (ISLs)
- Integrated device manager
- End-to-end storage topology view from client to LUN
- Storage networking health color-coding on topology views
- Storage bandwidth
- Storage enclosure and VM visibility
- Web-based zoning and IVR zoning configuration
- SAN host path redundancy feature
- Slow-drain analysis features
- Integration and discovery for popular storage LUN manufacturers
- End-to-end flow visualization
- Fabric bootstrap: day-0 provisioning
- Dashboards for a custom summary view of LAN and SAN domains and topology groups
Figure 10-23 shows a screenshot from the topology view of the Cisco DCNM.
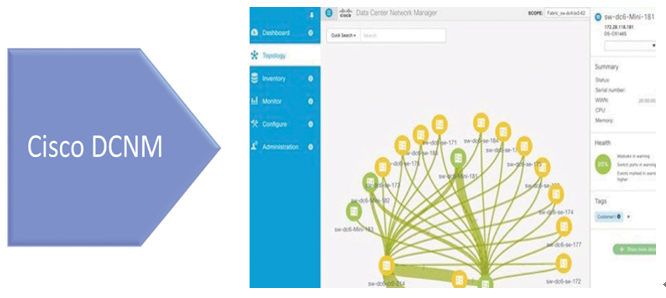
Figure 10-23 Cisco DCNM
Cisco MDS 9000 multilayer SAN switches are designed based on the switched fabric flexible hardware architecture. This is combined with the use of hardware buffers, queues, and a virtual output queueing technique with a central arbiter to allow for cut-through speeds, avoidance of head-of-line blocking, security, stability, and scalability.
Here are some of the important benefits of the Cisco MDS 9000 series SAN switches:
- Industry-leading scalability: Up to 768 line-rate 32G Fibre Channel ports to deliver both scale and performance.
- Deep visibility: Built-in hardware-based analytics enable faster troubleshooting and resolution.
- Flexibility: Multiprotocol support, support for 32Gbps Fibre Channel, and readiness for 64Gbps Fibre Channel, 40G Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE), and Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) over fabric.
Figure 10-24 shows the Cisco MDS 9000 series of switches.
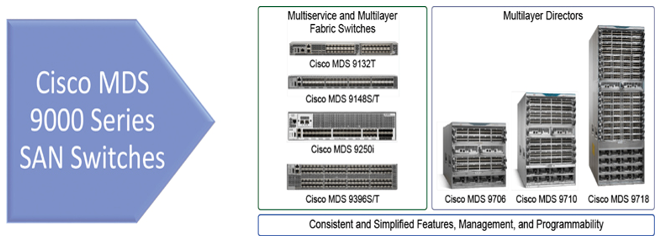
Figure 10-24 Cisco MDS 9000 Series SAN Switches
Here are the current Cisco MDS 9000 switches:
- Cisco MDS 9718 Multilayer Director
- Cisco MDS 9710 Multilayer Director
- Cisco MDS 9706 Multilayer Director
- Cisco MDS 9250i Multiservice Fabric Switch
- Cisco MDS 9396T Multilayer Fabric Switch
- Cisco MDS 9396S Multilayer Fabric Switch
- Cisco MDS 9148T Multilayer Fabric Switch
- Cisco MDS 9148S Multilayer Fabric Switch
- Cisco MDS 9132T Multilayer Fabric Switch