Storage Area Network (SAN)
Storage area networks (SANs) are specialized, separate physical infrastructures, created to provide fast, low-latency, secure and reliable communication between the initiators and the targets (that is, the hosts and the storage systems). The storage systems used are professional, specialized storage systems that support the Fibre Channel Protocol and have HBAs to connect to the SAN.
The initiators usually are the servers in the data center because the applications run on them, and therefore they are the consumer of the services of the storage systems. The servers also need to be physically equipped with HBAs to connect to the SAN.
The communication component of the SAN is built by using specialized switches. These switches use the Fibre Channel Protocol for the communication between the initiators and the servers connected to them. The three major participants—the initiators, the targets, and the FC switches—create the SAN fabric. The fabric is not only the sum of the physical components but also the convergence of all the needed processes and services for the FC Protocol to run in this environment.
The FC switches for physical connectivity use fiber optics and special FC transceivers. This creates a very fast infrastructure, as the speeds supported can be 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, or 64Gbps.
The Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is the transport protocol used in the SAN. It provides a high-speed, secure, and lossless exchange of data, sent in blocks, in the form of SCSI commands. It is standardized from the Technical Committee T11 of the INCITS, an ANSI-accredited standards committee. Something interesting is that although nowadays the FCP is used to transport the SCSI commands, it is still a transport protocol and can also be used to transport the communication for other protocols, as long as you can encapsulate the data units of another protocol in FC frames. This is not common; however, it is just mentioned here to make a clear difference between the transport, the FCP, and the block-storage protocol, in this case the SCSI protocol.
The FCP was standardized in 1988, with further approval from ANSI in 1994. Cisco Systems entered the SAN market in 2002 with the acquisition of Andiamo Systems, Inc., which is the company that developed the first intelligent multilayer storage switches. The same year, Cisco released the Cisco MDS switches, FC switches running the SAN-OS (Cisco’s implementation of FCP).
A SAN, illustrated in Figure 10-7, provides a lot of benefits for data centers:
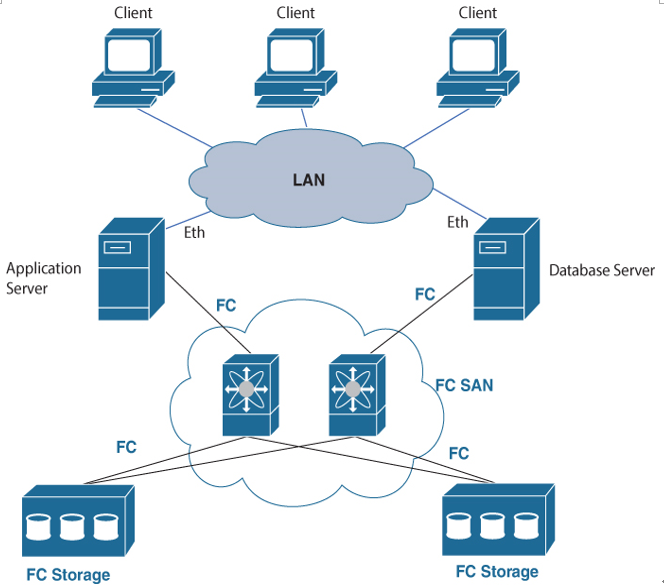
Figure 10-7 Fibre Channel Storage Area Network
- Dedicated infrastructure for storage communication
- High performance and low latency
- Secure and lossless
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO) compared to DAS
- Controlled sharing of the storage resources
- Easier and faster backup
- Up to 16 million devices
- Segments of up to 10 km without extenders